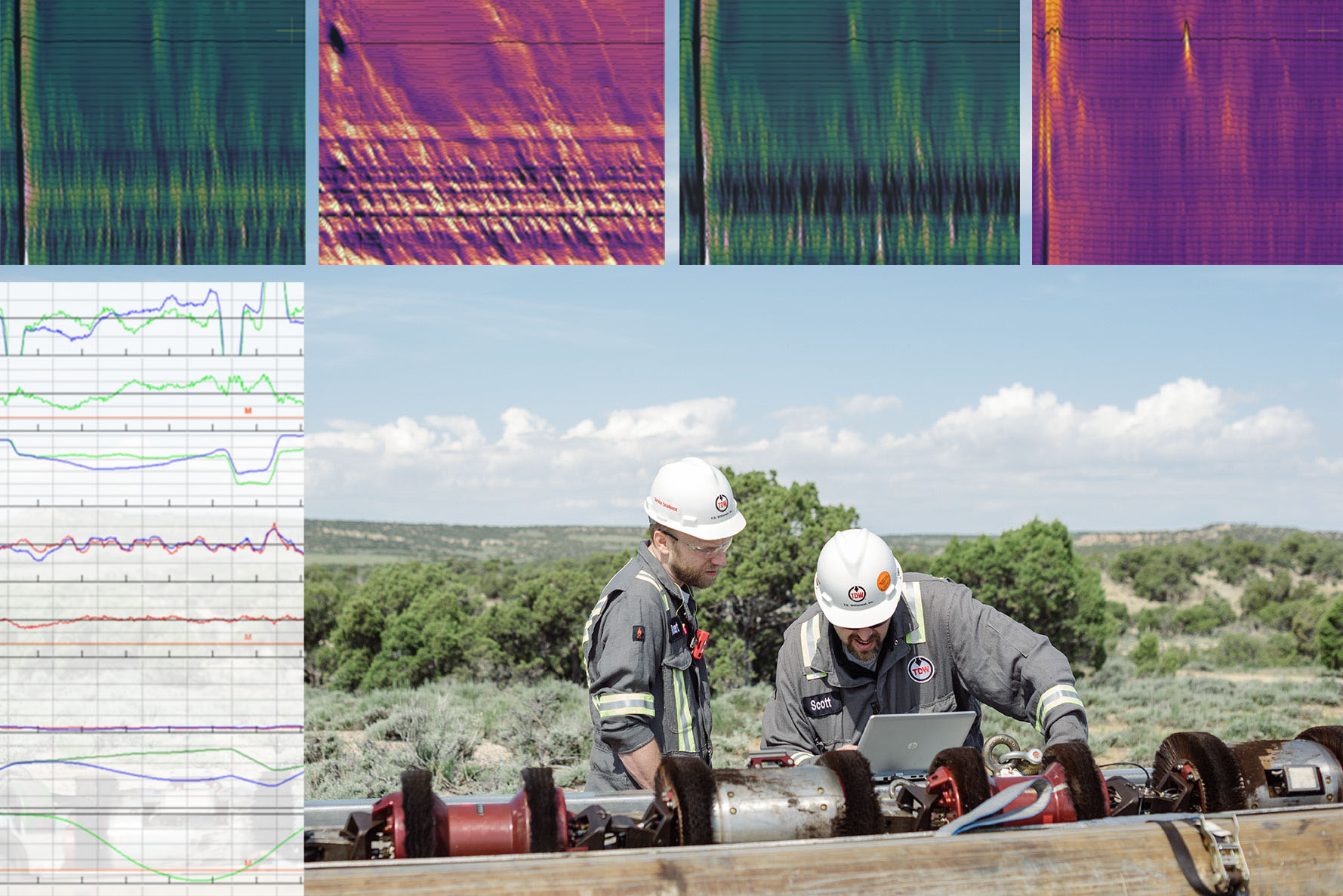
Low Field Magnetic Flux Leakage (LFM)
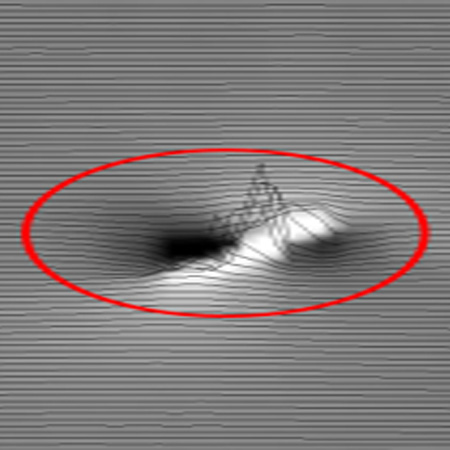
Low Field Magnetic Flux Leakage - known as LFM - Identifies changes in steel microstructure resulting from manufacture or milling. It also detects dent re-rounding, which can raise the severity of a dent and lead to cracking; hard spots, a localized hardening of the steel due to rapid cooling; and sensitivity to chemical and metallurgical properties of the steel itself.
LFM is also a key dataset in pipe joint classification (PJC), a methodology for grouping pipe joints with the same fingerprint for material documentation and discrepancy analysis as defined by the American Petroleum Institute’s API 1163.
Key Features
- Introduces a controlled lower magnetic flux leakage field that is sensitive to steel microstructure variations and metallurgical characteristics
- Facilitates the prioritization of higher risk dent anomalies
Sizes
- 8-inch through 30-inch

Low Field Magnetic Flux Leakage - known as LFM - Identifies changes in steel microstructure resulting from manufacture or milling. It also detects dent re-rounding, which can raise the severity of a dent and lead to cracking; hard spots, a localized hardening of the steel due to rapid cooling; and sensitivity to chemical and metallurgical properties of the steel itself.
LFM is also a key dataset in pipe joint classification (PJC), a methodology for grouping pipe joints with the same fingerprint for material documentation and discrepancy analysis as defined by the American Petroleum Institute’s API 1163.
Key Features
- Introduces a controlled lower magnetic flux leakage field that is sensitive to steel microstructure variations and metallurgical characteristics
- Facilitates the prioritization of higher risk dent anomalies
Sizes
- 8-inch through 30-inch



