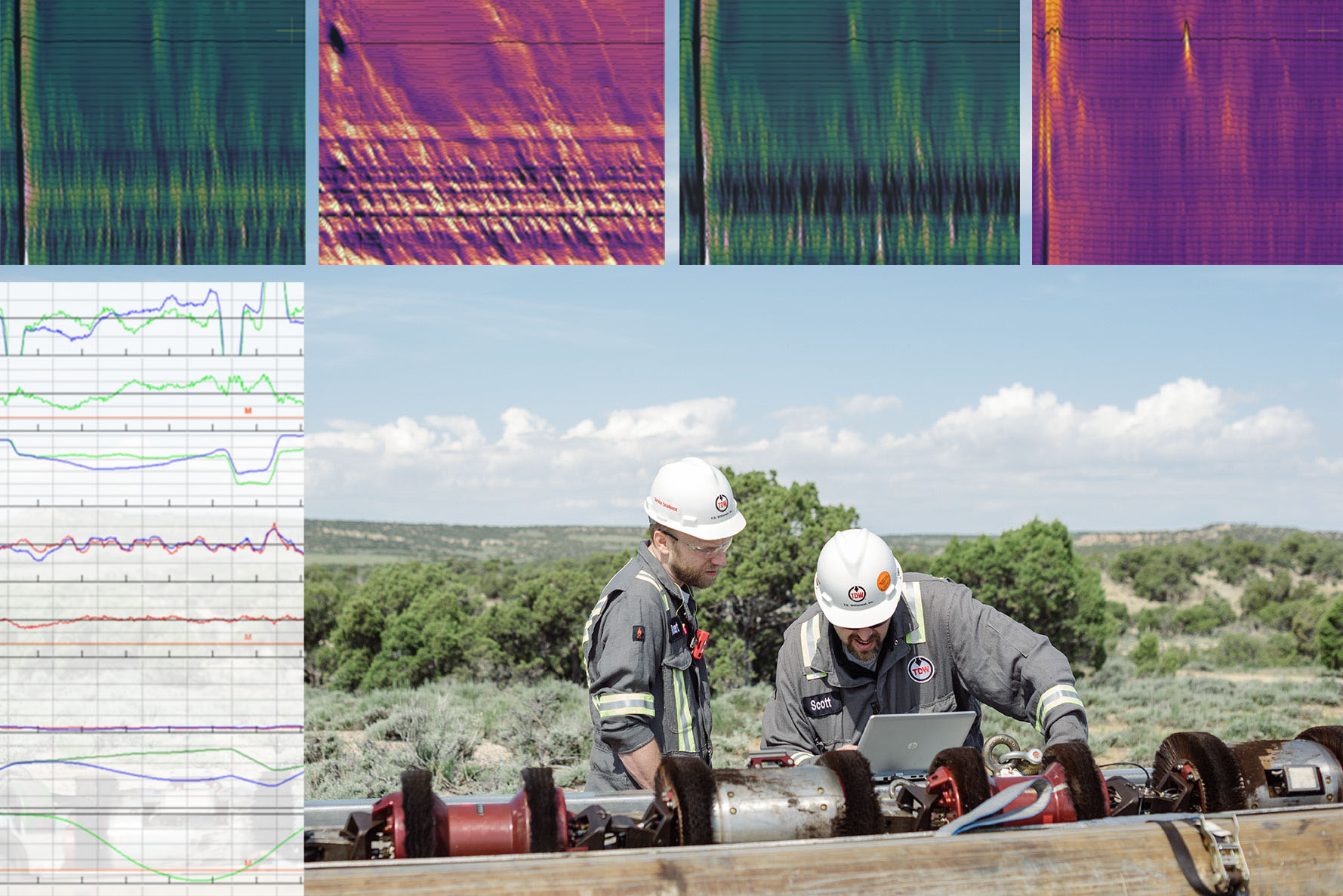
MDS™ Pro Platform

Identifying pipeline threats is the first step in pipeline safety. That includes detecting features which are interacting, meaning they occur simultaneously and pose a greater risk when combined than they would individually. Some ILI tools may not detect interacting features, leaving operators with an incomplete picture of a pipeline's integrity.
MDS™ Pro closes these detection gaps by integrating multiple in-line inspection (ILI) technologies on a single platform, reducing risk, increasing accuracy and providing a more comprehensive assessment.
The updated MDS Pro with Ultra Res MFL technology expands the detection capabilities of the tool even further. Ultra Res MFL brings the highest density of axial MFL sensors, enhancing detection performance for pinhole anomalies, complex corrosion and other features.

Key Features
- Features our most advanced combination of technologies to identify threats not detected by Axial MFL alone.
- Three unique magnetic technologies (Ultra Res Axial MFL, SpirALL® MFL, and residual or low field MFL).
- Now with Ultra Res MFL technology, resulting in enhanced pinhole sizing and additional insight into complex corrosion.
- Provides enhanced seam assessment for selective seam weld corrosion (SSWC) and axially planar crack-like features.
- Offers improved classification for gouges and non-axial stress corrosion cracking.
- Overcomes limitations encountered when using independent inspection technologies.
- Provides a foundation for establishing a material verification program.
Technologies

SpirALL® MFL (SMFL)
Detects, identifies and sizes axially oriented metal loss and planar anomalies.

Ultra Res Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
Detects, identifies and sizes metal loss and circumferential planar anomalies.
Low Field MFL (LFM)
Identifies material property changes resulting from manufacture, milling or mechanical working.
XYZ Mapping (XYZ)
Measures pipe centerline, provides highly accurate coordinates for all reported features, and enables bending strain analysis.

Deformation (DEF)
Detects, identifies and sizes bore changes such as dents, ovalities, expansions and wrinkles.

Identifying pipeline threats is the first step in pipeline safety. That includes detecting features which are interacting, meaning they occur simultaneously and pose a greater risk when combined than they would individually. Some ILI tools may not detect interacting features, leaving operators with an incomplete picture of a pipeline's integrity.
MDS™ Pro closes these detection gaps by integrating multiple in-line inspection (ILI) technologies on a single platform, reducing risk, increasing accuracy and providing a more comprehensive assessment.
The updated MDS Pro with Ultra Res MFL technology expands the detection capabilities of the tool even further. Ultra Res MFL brings the highest density of axial MFL sensors, enhancing detection performance for pinhole anomalies, complex corrosion and other features.

Key Features
- Features our most advanced combination of technologies to identify threats not detected by Axial MFL alone.
- Three unique magnetic technologies (Ultra Res Axial MFL, SpirALL® MFL, and residual or low field MFL).
- Now with Ultra Res MFL technology, resulting in enhanced pinhole sizing and additional insight into complex corrosion.
- Provides enhanced seam assessment for selective seam weld corrosion (SSWC) and axially planar crack-like features.
- Offers improved classification for gouges and non-axial stress corrosion cracking.
- Overcomes limitations encountered when using independent inspection technologies.
- Provides a foundation for establishing a material verification program.
Technologies

SpirALL® MFL (SMFL)
Detects, identifies and sizes axially oriented metal loss and planar anomalies.

Ultra Res Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
Detects, identifies and sizes metal loss and circumferential planar anomalies.

Low Field MFL (LFM)
Identifies material property changes resulting from manufacture, milling or mechanical working.

XYZ Mapping (XYZ)
Measures pipe centerline, provides highly accurate coordinates for all reported features, and enables bending strain analysis.

Deformation (DEF)
Detects, identifies and sizes bore changes such as dents, ovalities, expansions and wrinkles.






